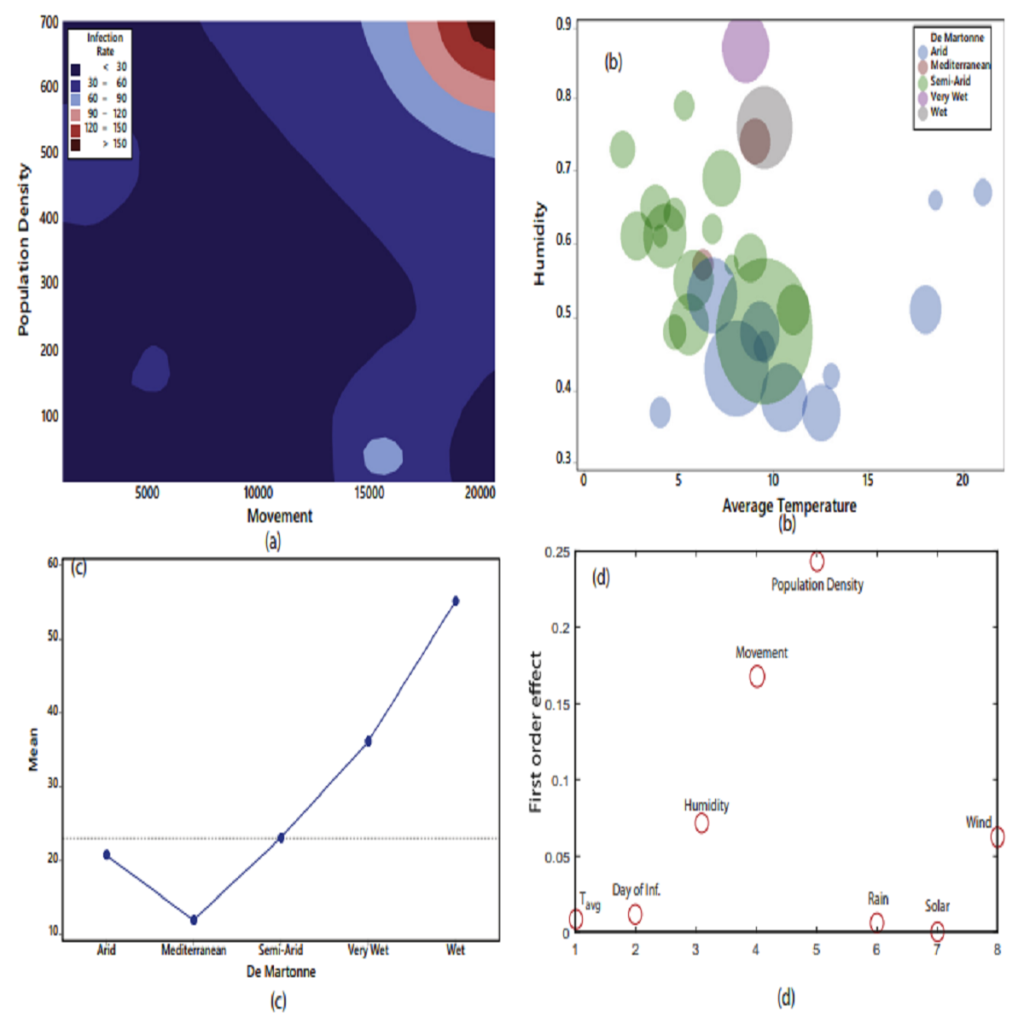
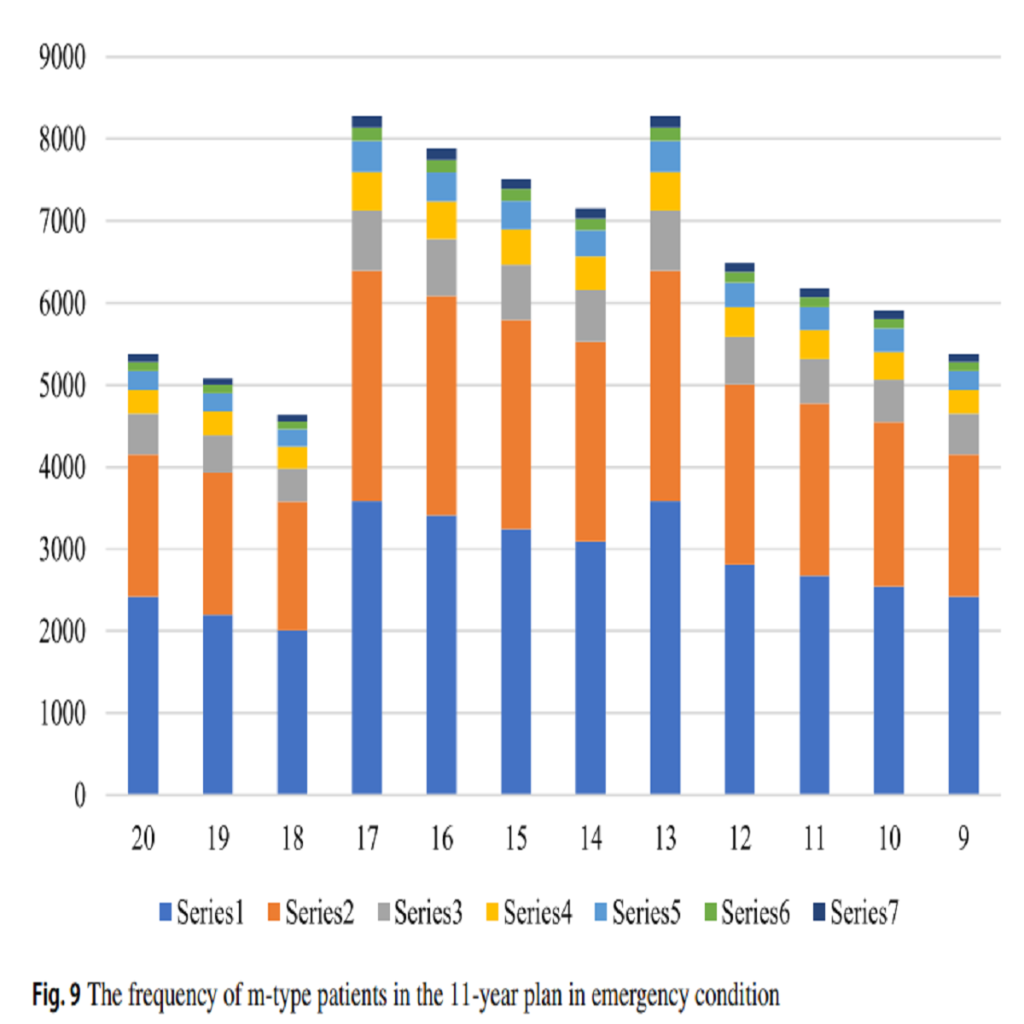
SARS CoV-2 (COVID-19) Coronavirus cases are confirmed throughout the world and millions of people are being put into quarantine. A better understanding of the effective parameters in infection spreading can bring about a logical measurement toward COVID-19. The effect of climatic factors on spreading of COVID-19 can play an important role in the new Coronavirus outbreak. In this study, the main parameters, including the number of infected people with COVID-19, population density, intra-provincial movement, and infection days to end of the study period, average temperature, average precipitation, humidity, wind speed, and average solar radiation investigated to understand how can these parameters effects on COVID-19 spreading in Iran? The Partial correlation coefficient (PCC) and Sobol’-Jansen methods are used for analyzing the effect and correlation of variables with the COVID-19 spreading rate …
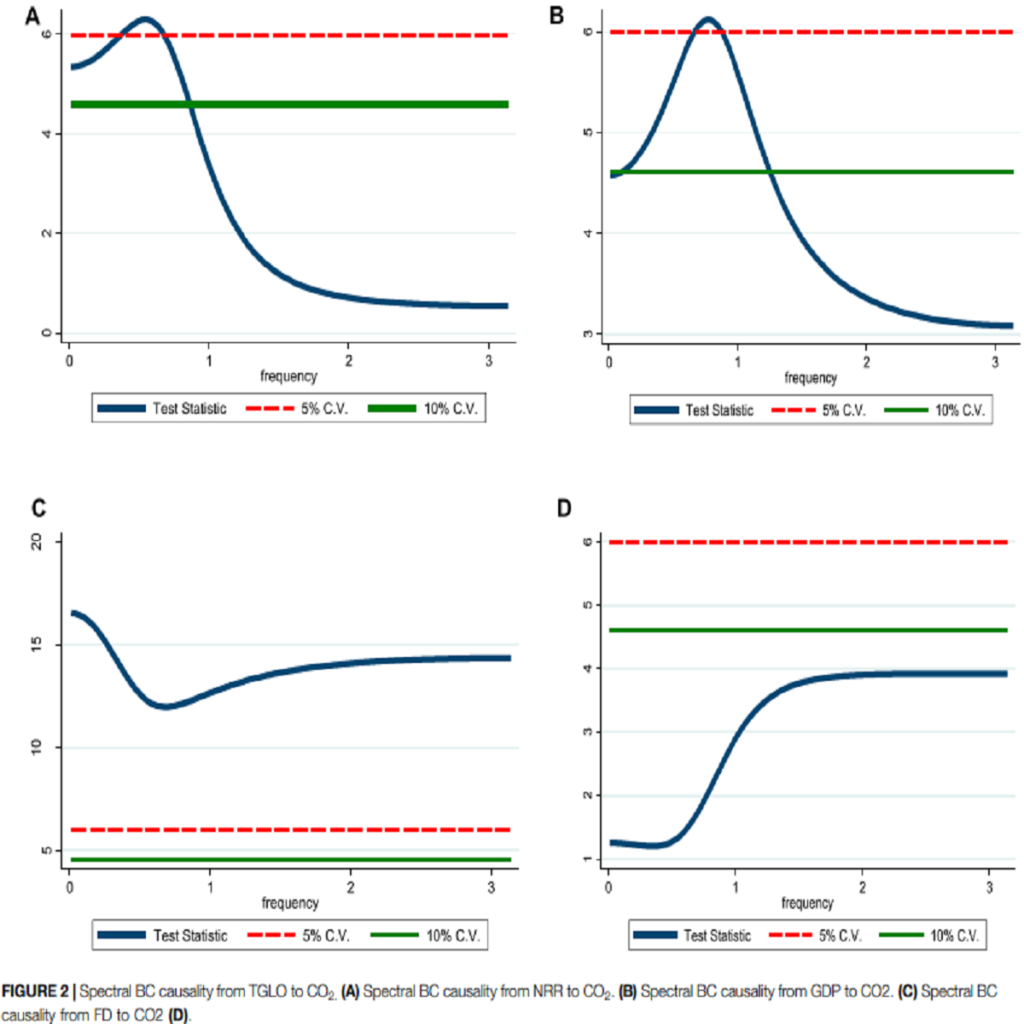
As the world continues to be a globalized society, there have been variations in environmental quality, but studies including trade globalization into the environmental policy framework remain limited. Therefore, employing the time series dataset of Uruguay over the period between 1980 and 2018, this current study investigates the effect of trade globalization, natural resources rents, economic growth, and financial development on carbon emissions. By employing the bounds testing procedures in combination with the critical approximation p-values of Kripfganz and Schneider (2018), ARDL estimators, and spectral causality test to achieve the goal of this research. The outcomes of the ARDL bounds test confirm a longrun connection between carbon emissions and its determinants. Moreover, from the outcome of the ARDL approach, we observed that trade globalization, economic growth, natural resources contribute to carbon emissions in Uruguay. Furthermore, we uncover that financial development does not impact environmental deterioration in Uruguay. The outcome of the spectral causality test detected that trade globalization, economic growth, and natural resources forecast carbon emissions with the exclusion of financial development. Based on the outcome, this study suggests that policies should be tailored towards international trade must be reassessed, and the restrictions placed on the exportation of polluting-intensive commodities must be reinforced
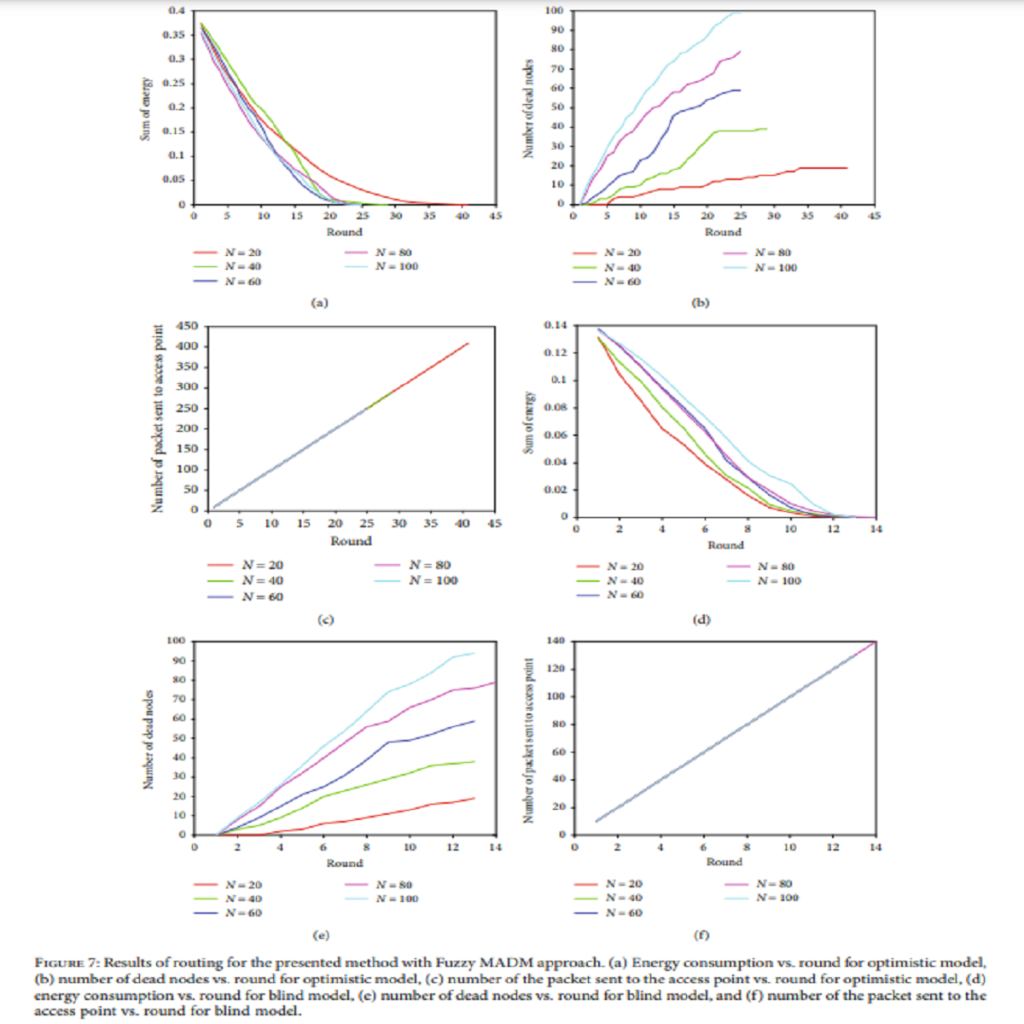
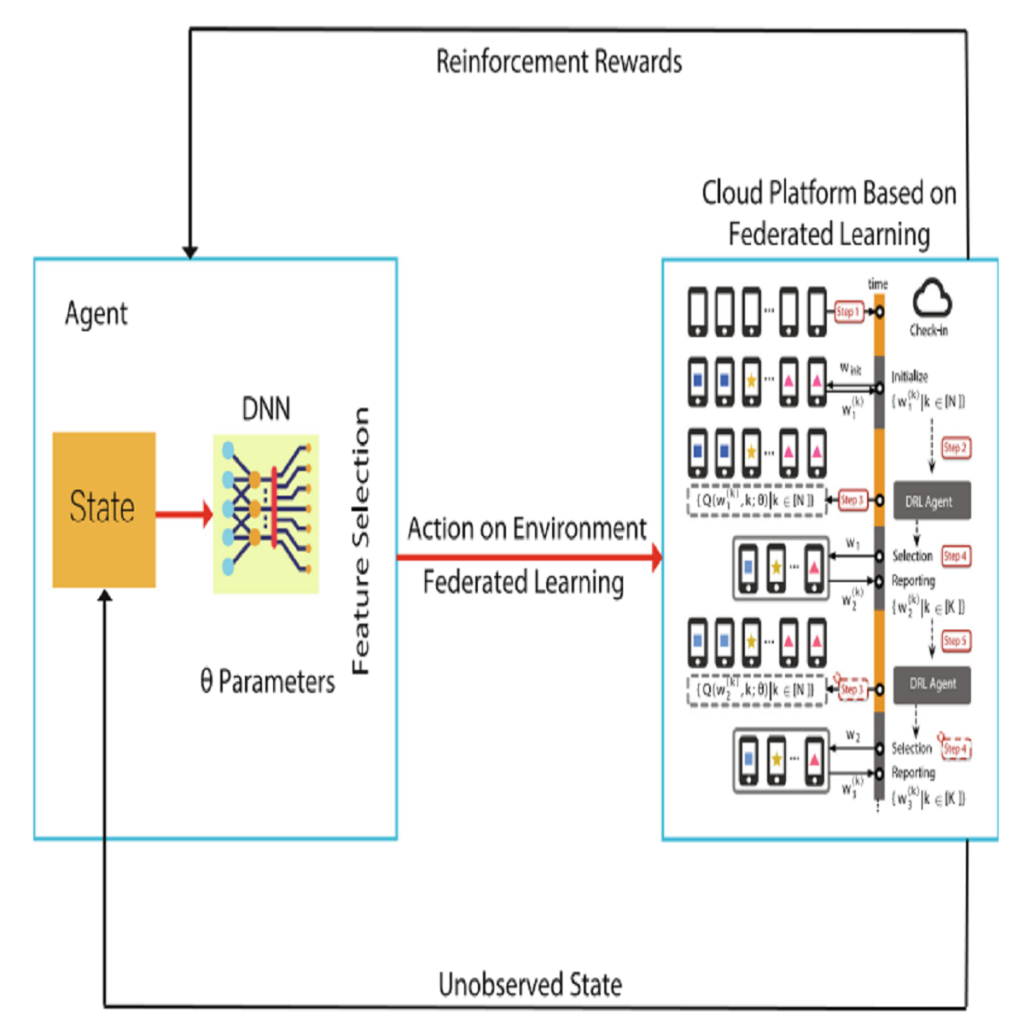
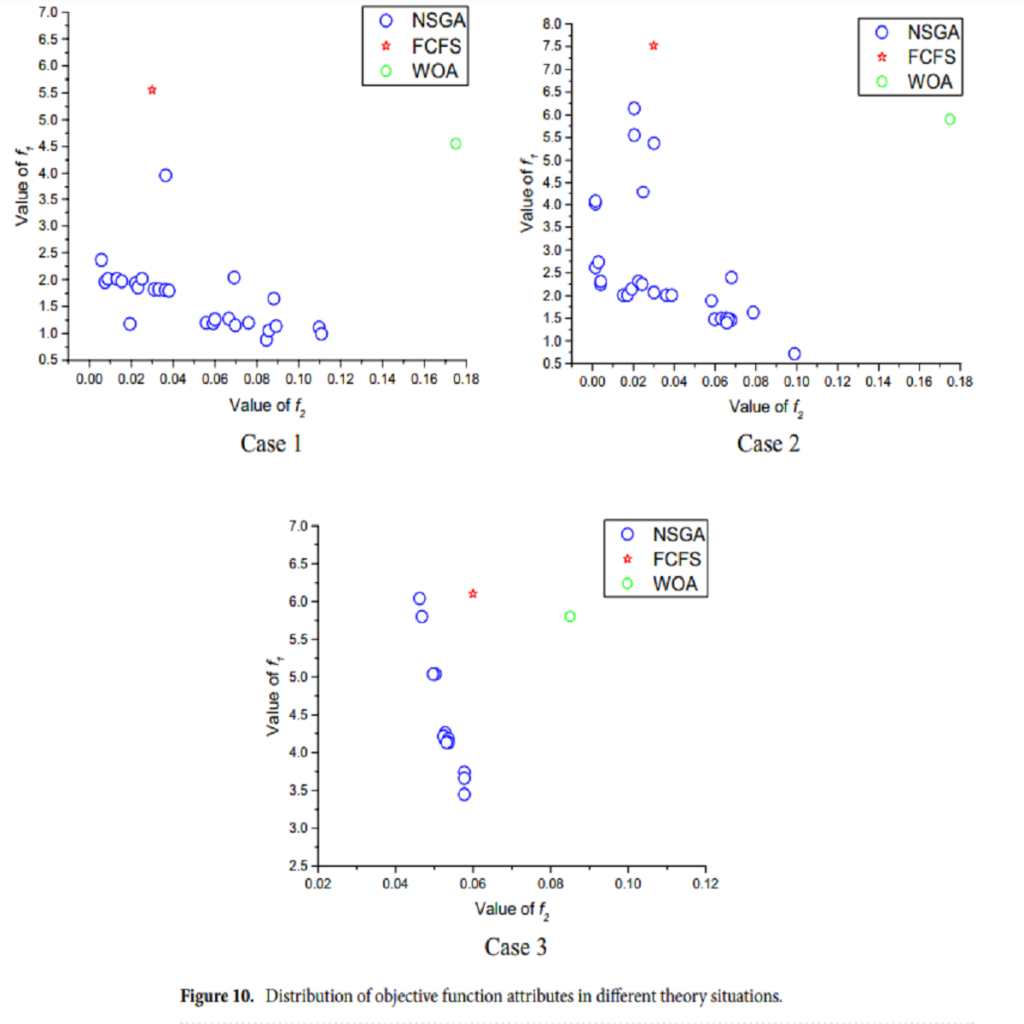
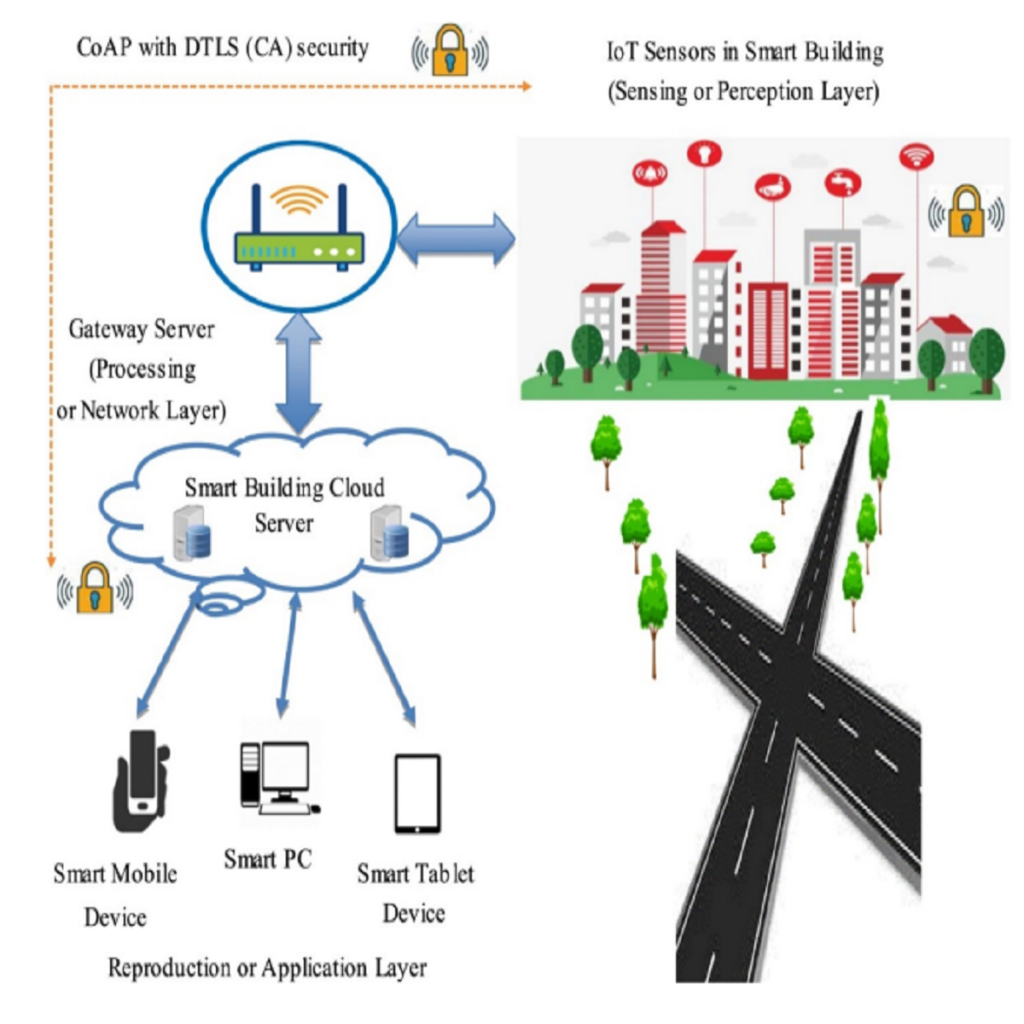
Advances in wireless technologies and small computing devices, wireless sensor networks can be superior technology in many applications. Energy supply constraints are one of the most critical measures because they limit the operation of the sensor network; therefore, the optimal use of node energy has always been one of the biggest challenges in wireless sensor networks. Moreover, due to the limited lifespan of nodes in WSN and energy management, increasing network life is one of the most critical challenges in WSN. In this investigation, two computational distributions are presented for a dynamic wireless sensor network; in this fog-based system, computing load was distributed using the optimistic and blind method between fog networks. The presented method with the main four steps is called Distribution-Map-Transfer-Combination (DMTC) method. Also, Fuzzy Multiple Attribute Decision-Making (Fuzzy MADM) is used for clustering and routing network based on the presented distribution methods. Results show that the optimistic method outperformed the blind one and reduced energy consumption, especially in extensive networks; however, in small WSNs, the blind scheme resulted in an energy efficiency network. Furthermore, network growth leads optimistic WSN to save higher energy in comparison with blinded ones. Based on the results of complexity analysis, the presented optimal and blind methods are improved by 28% and 48%, respectively.
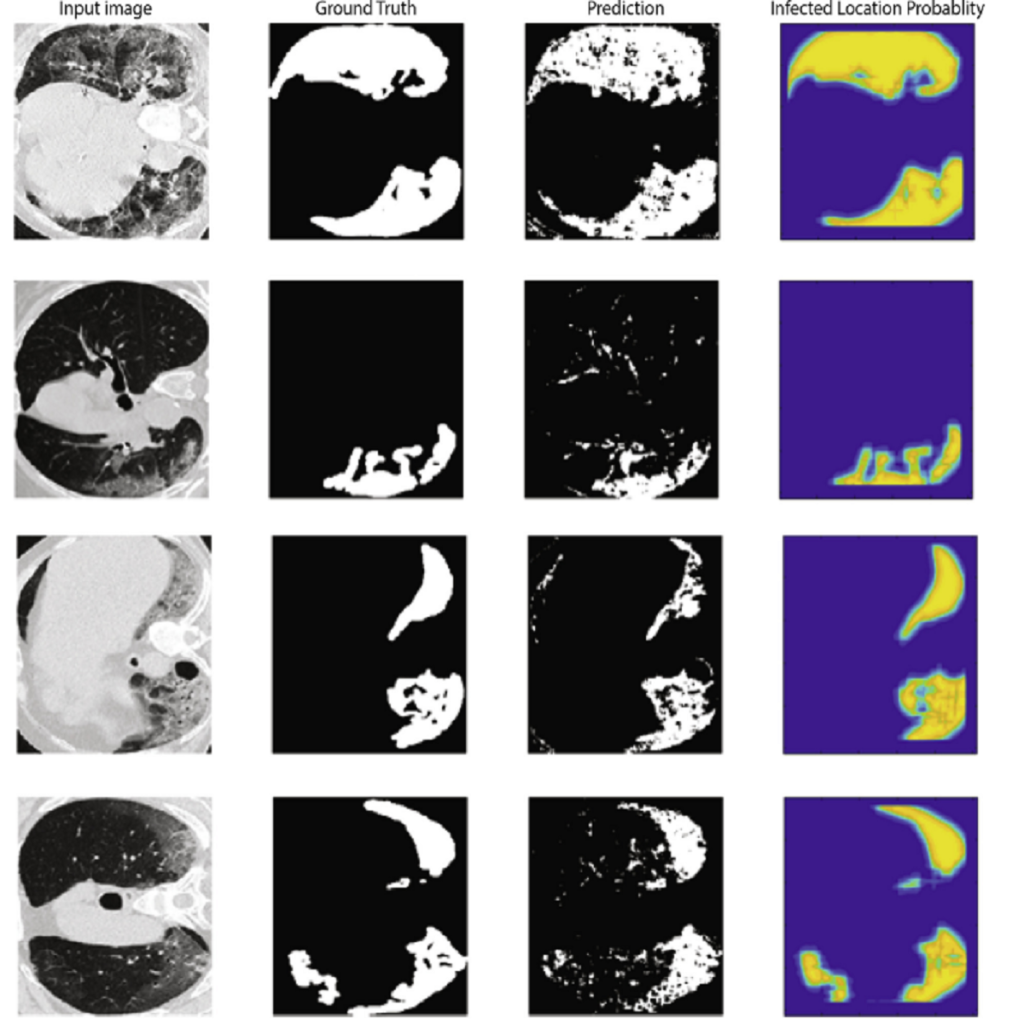
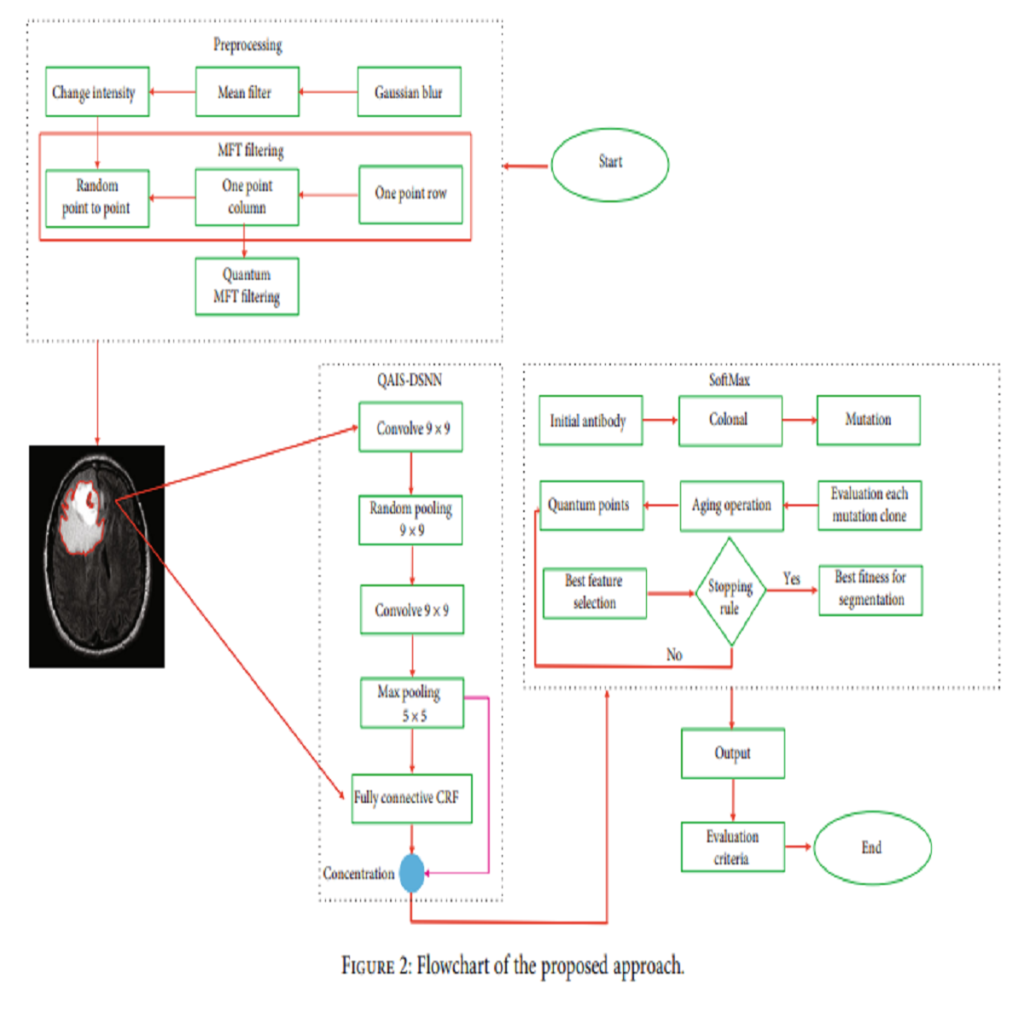
Tumor segmentation in brain MRI images is a noted process that can make the tumor easier to diagnose and lead to effective radiotherapy planning. Providing and building intelligent medical systems can be considered as an aid for physicians. In many cases, the presented methods’ reliability is at a high level, and such systems are used directly. In recent decades, several methods of segmentation of various images, such as MRI, CT, and PET, have been proposed for brain tumors. Advanced brain tumor segmentation has been a challenging issue in the scientific community. The reason for this is the existence of various tumor dimensions with disproportionate boundaries in medical imaging. This research provides an optimized MRI segmentation method to diagnose tumors. It first offers a preprocessing approach to reduce noise with a new method called Quantum Matched-Filter Technique (QMFT). Then, the deep spiking neural network (DSNN) is implemented for segmentation using the conditional random field structure. However, a new algorithm called the Quantum Artificial Immune System (QAIS) is used in its SoftMax layer due to its slowness and nonsegmentation and the identification of suitable features for selection and extraction. The proposed approach, called QAIS-DSNN, has a high ability to segment and distinguish brain tumors from MRI images. The simulation results using the BraTS2018 dataset show that the accuracy of the proposed approach is 98.21%, average error-squared rate is 0.006, signal-to-noise ratio is 97.79 dB, and lesion structure criteria including the tumor nucleus are 80.15%. The improved tumor is 74.50%, and …
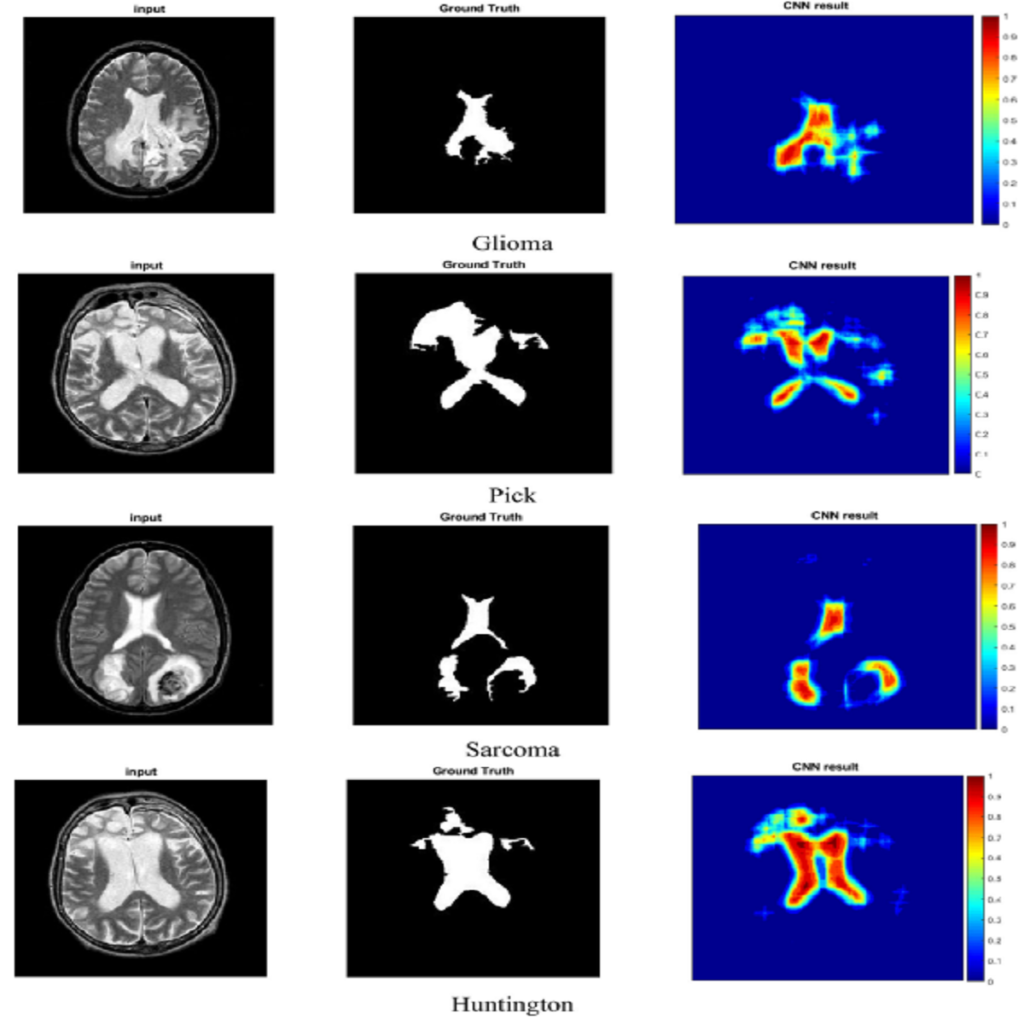
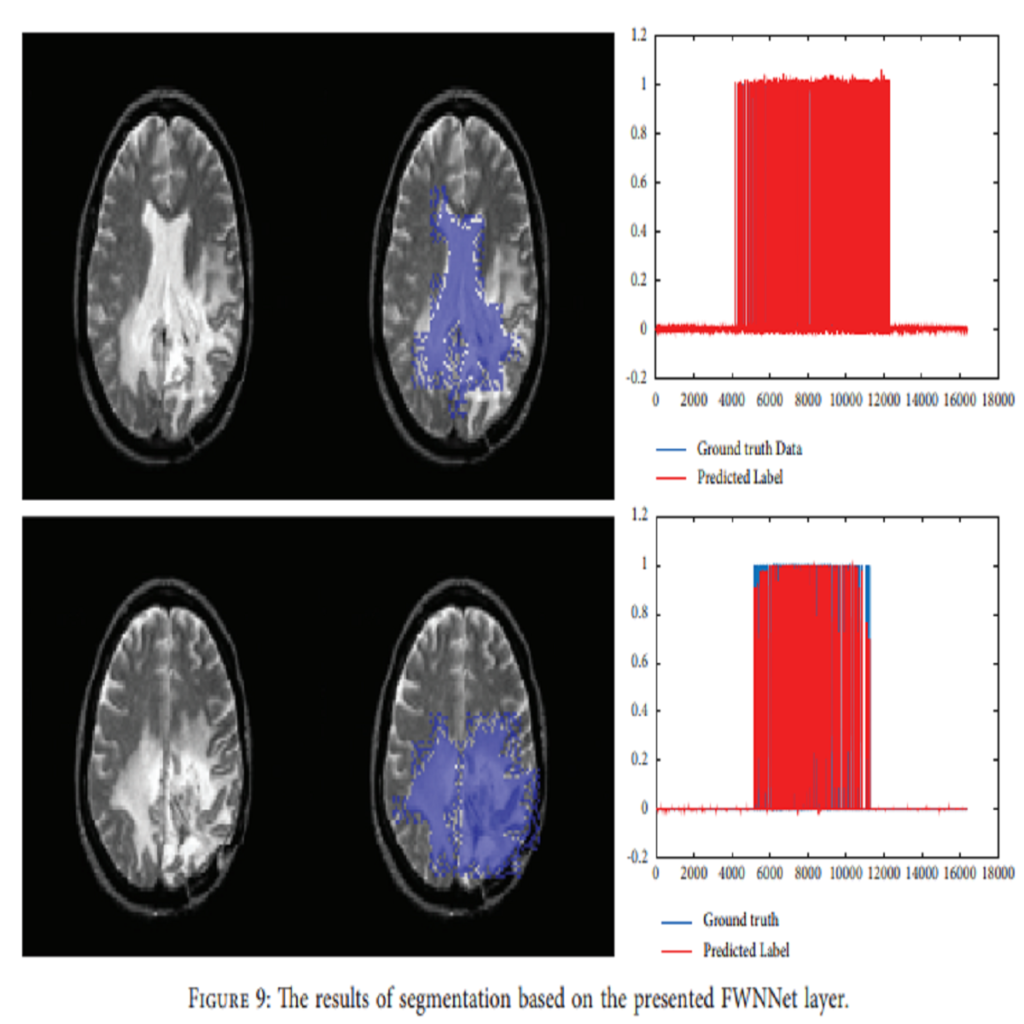
In this paper, we present a novel classifier based on fuzzy logic and wavelet transformation in the form of a neural network. This classifier includes a layer to predict the numerical feature corresponded to labels or classes. The presented classifier is implemented in brain tumor diagnosis. For feature extraction, a fractal model with four Gaussian functions is used. The classification is performed on 2000 MRI images. Regarding the results, the accuracy of the DT, KNN, LDA, NB, MLP, and SVM is 93.5%, 87.6%, 61.5%, 57.5%, 68.5%, and 43.6%, respectively. Based on the results, the presented FWNNet illustrates the highest accuracy of 100% with the fractal feature extraction method and brain tumor diagnosis based on MRI images. Based on the results, the best classifier for diagnosis of the brain tumor is FWNNet architecture. However, the second and third high-performance classifiers are the DT and KNN, respectively. Moreover, the presented FWNNet method is implemented for the segmentation of brain tumors. In this paper, we present a novel supervised segmentation method based on the FWNNet layer. In the training process, input images with a sweeping filter should be reshaped to vectors that correspond to reshaped ground truth images. In the training process, we performed a PSO algorithm to optimize the gradient descent algorithm. For this purpose, 80 MRI images are used to segment the brain tumor. Based on the results of the ROC curve, it can be estimated that the presented layer can segment the brain tumor with a high true-positive rate.
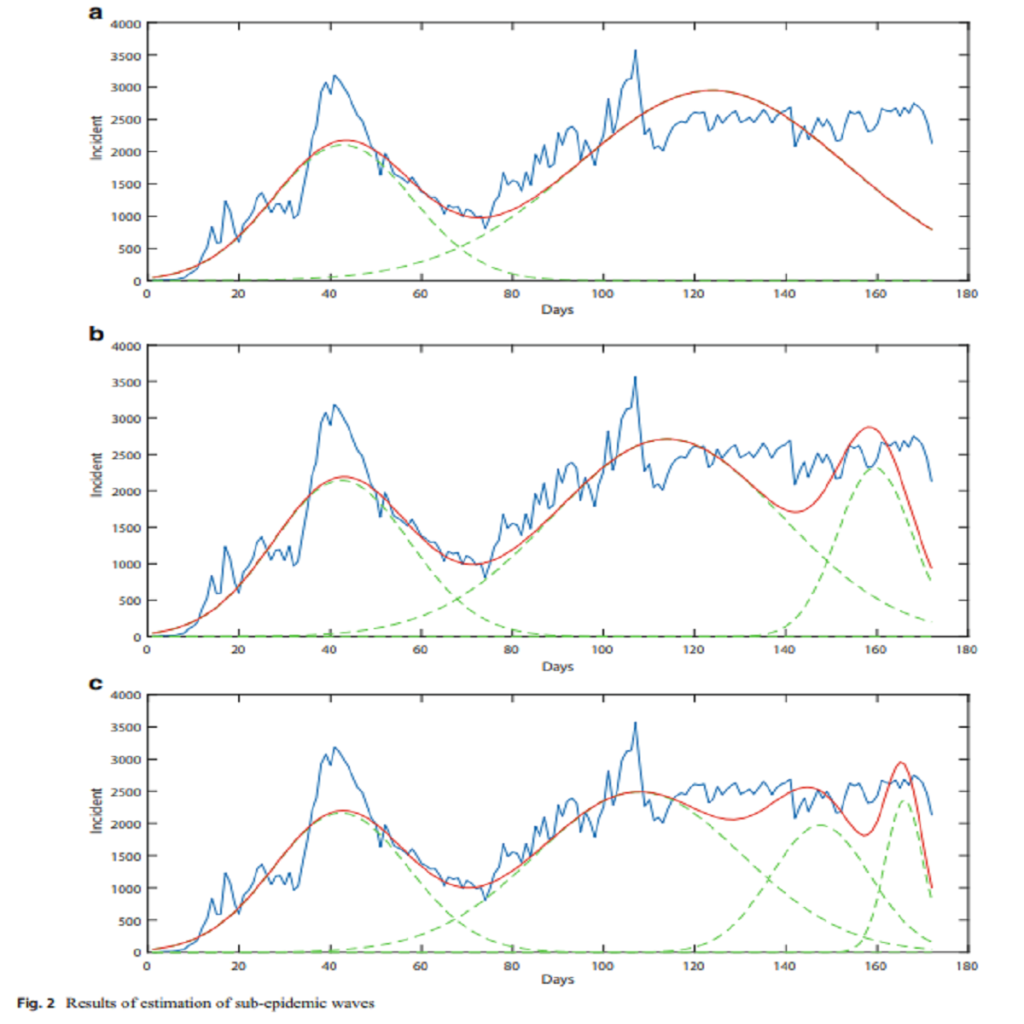
The COVID-19 pandemic is one of the contagious diseases involving all the world in 2019–2020. Also, all people are concerned about the future of this catastrophe and how the continuous outbreak can be prevented. Some countries are not successful in controlling the outbreak; therefore, the incidence is observed in several peaks. In this paper, firstly single-peak SIR models are used for historical data. Regarding the SIR model, the termination time of the outbreak should have been in early June 2020. However, several peaks invalidate the results of single-peak models. Therefore, we should present a model to support pandemics with several extrema. In this paper, we presented the generalized logistic growth model (GLM) to estimate sub-epidemic waves of the COVID-19 outbreak in Iran. Therefore, the presented model simulated scenarios of two, three, and four waves in the observed incidence. In the…
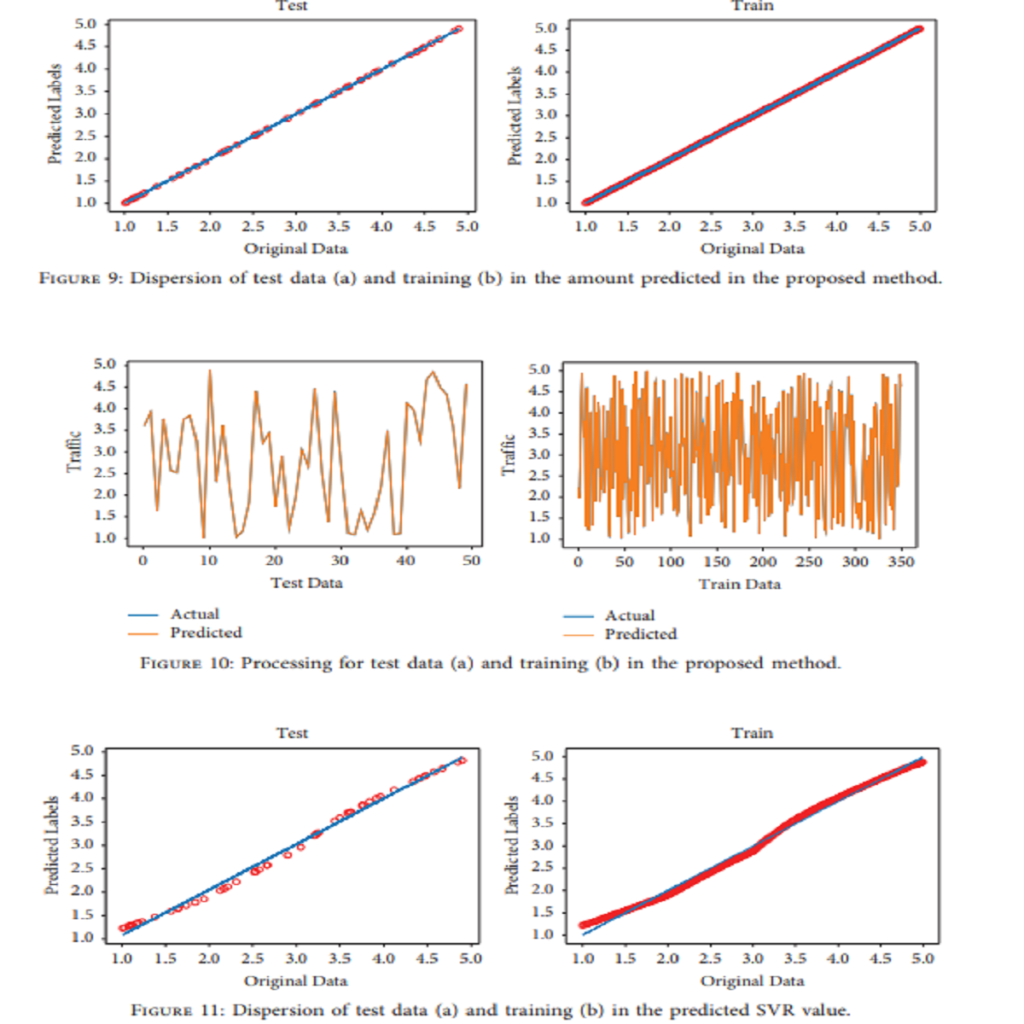
Traffic prediction is critical to expanding a smart city and country because it improves urban planning and traffic management. This prediction is very challenging due to the multifactorial and random nature of traffic. This study presented a method based on ensemble learning to predict urban traffic congestion based on weather criteria. We used the NAS algorithm, which in the output based on heuristic methods creates an optimal model concerning input data. We had 400 data, which included the characteristics of the day’s weather, including six features: absolute humidity, dew point, visibility, wind speed, cloud height, and temperature, which in the final column is the urban traffic congestion target. We have analyzed linear regression with the results obtained in the project; this method was more efficient than other regression models. This method had an error of 0.00002 in terms of MSE criteria and SVR, random forest, and MLP methods, which have error values of 0.01033, 0.00003, and 0.0011, respectively. According to the MAE criterion, this method has a value of 0.0039. The other methods have obtained values of 0.0850, 0.0045, and 0.027, respectively, which show that our proposed model has a minor error than other methods and has been able to outpace the other models.
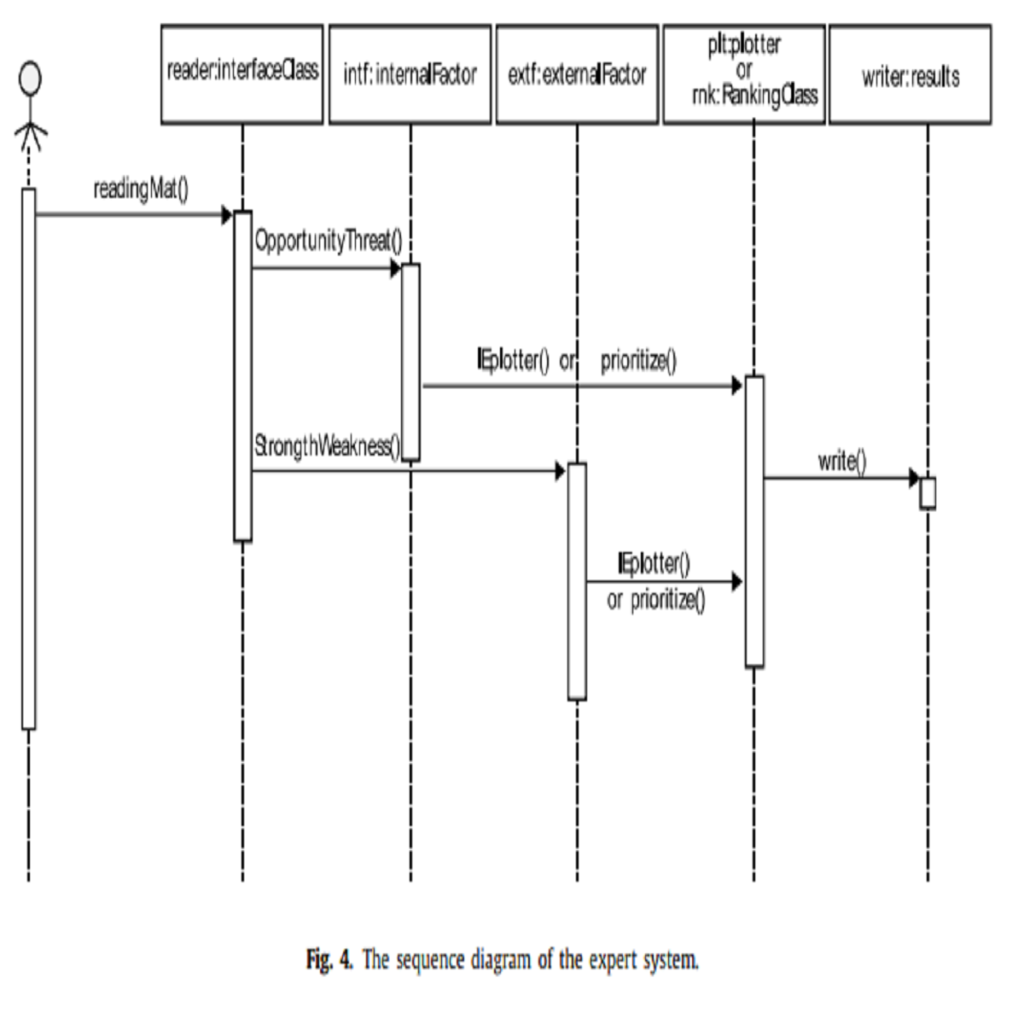
Using intelligent expert systems is a necessity for improving the situation of organizations. Since the process of identifying strategy in a strategic plan is time-consuming and costly, the role of expert systems in strategic planning is considerable. Managers utilize expert system to maintain and disseminate knowledge, training, and competition in the organization. Complicated expert system with long codes, practicality is not developable because of code complexity, but structural properties of the namespace and functions in C++ with using the object, solve this complexity and all codes are accessible without knowing based codes. In this paper using object orientation properties of C++, the expert can access, develop the system in the inference engine, practically without knowing based system code. According to the presented algorithm, the expert system designs a simple system for strategic planning in two steps, first …
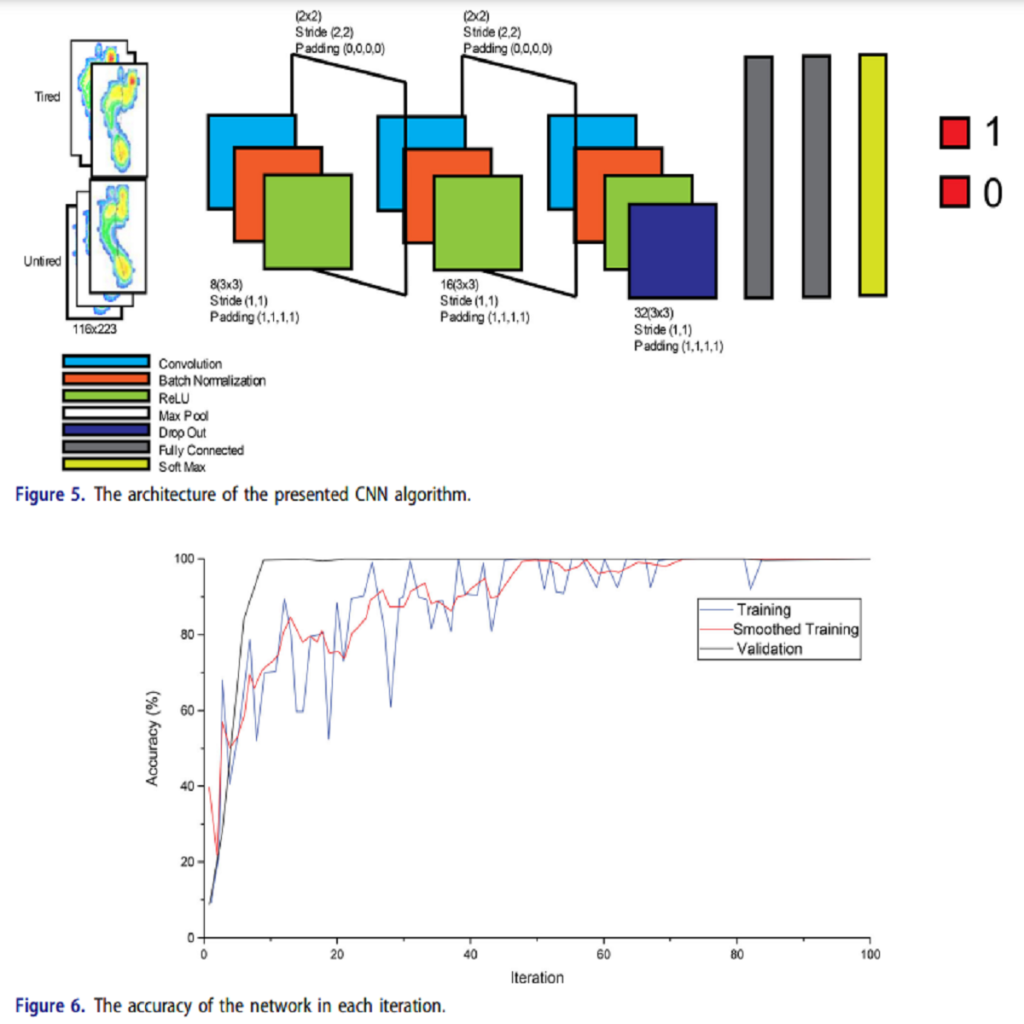
Fatigue is an essential criterion for physiotherapy in injured athletes. Muscle fatigue mechanism also is a crucial matter in designing a workout program. It is mainly related to physical injury, cerebrovascular accident, spinal cord injury, and rheumatologic disease. The leg is one of the organs in the body where fatigue is visible, and usually, the first fatigue traces in the human body are shown. The main objective of the article is to diagnosis tired and untired feet base on digital footprint images. Therefore, the foot images of students in the age group of 20–30 were examined. The device is a digital footprint scanner. This device includes a plate screen equipped with pressure sensors and footprints in the image. A treadmill is used for 8 min to tire our test individuals. Therefore, six methods of k-nearest-neighbor classifier, multilayer perceptron, support vector machine, naïve Bayesian learning, decision tree, and …
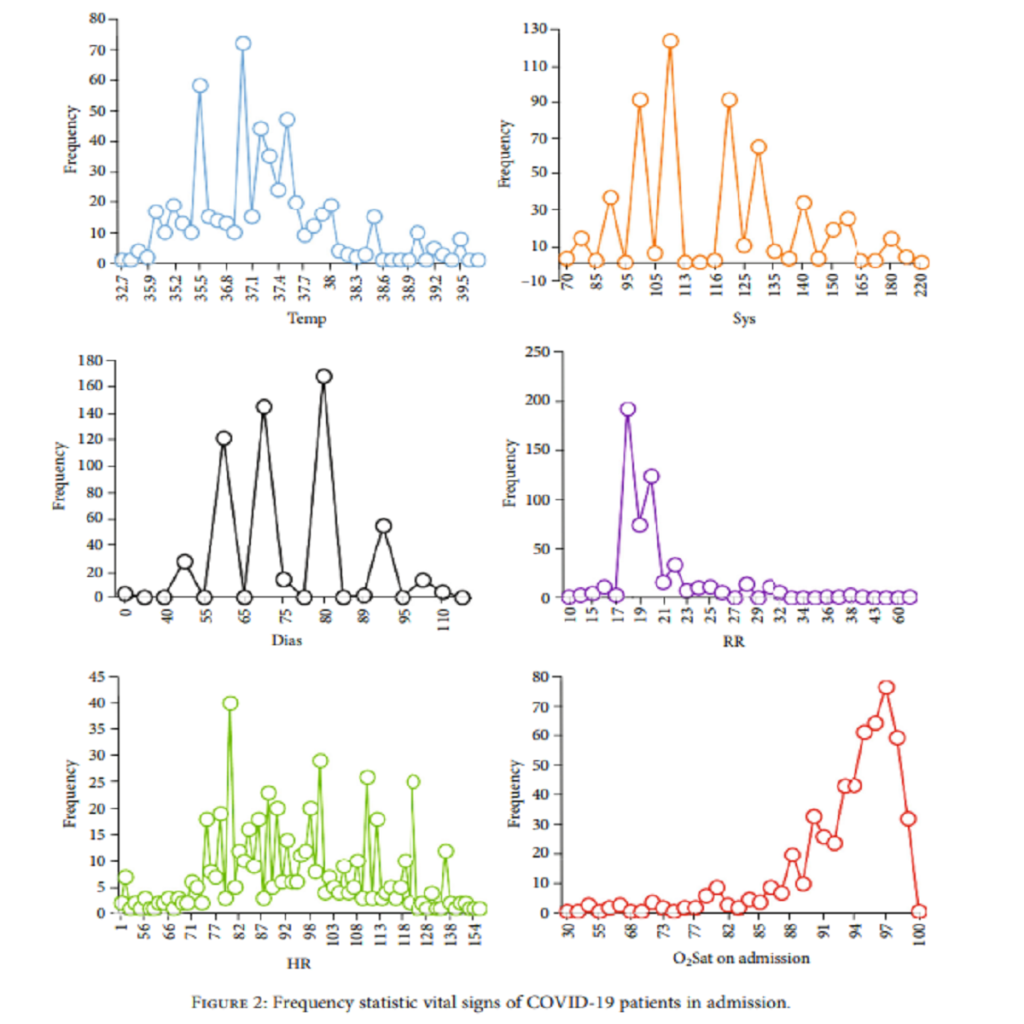
Statins can help COVID-19 patients’ treatment because of their involvement in angiotensin-converting enzyme-2. The main objective of this study is to evaluate the impact of statins on COVID-19 severity for people who have been taking statins before COVID-19 infection. The examined research patients include people that had taken three types of statins consisting of Atorvastatin, Simvastatin, and Rosuvastatin. The case study includes 561 patients admitted to the Razi Hospital in Ghaemshahr, Iran, during February and March 2020. The illness severity was encoded based on the respiratory rate, oxygen saturation, systolic pressure, and diastolic pressure in five categories: mild, medium, severe, critical, and death. Since 69.23% of participants were in mild severity condition, the results showed the positive effect of Simvastatin on COVID-19 severity for people that take Simvastatin before being infected by the COVID-19 virus. Also, systolic pressure for this case study is 137.31, which is higher than that of the total patients. Another result of this study is that Simvastatin takers have an average of 95.77 mmHg O2Sat; however, the O2Sat is 92.42, which is medium severity for evaluating the entire case study. In the rest of this paper, we used machine learning approaches to diagnose COVID-19 patients’ severity based on clinical features. Results indicated that the decision tree method could predict patients’ illness severity with 87.9% accuracy. Other methods, including the -nearest neighbors (KNN) algorithm, support vector machine (SVM), Naïve Bayes classifier, and discriminant analysis, showed accuracy levels of 80%, 68.8%, 61.1%, and 85.1 …
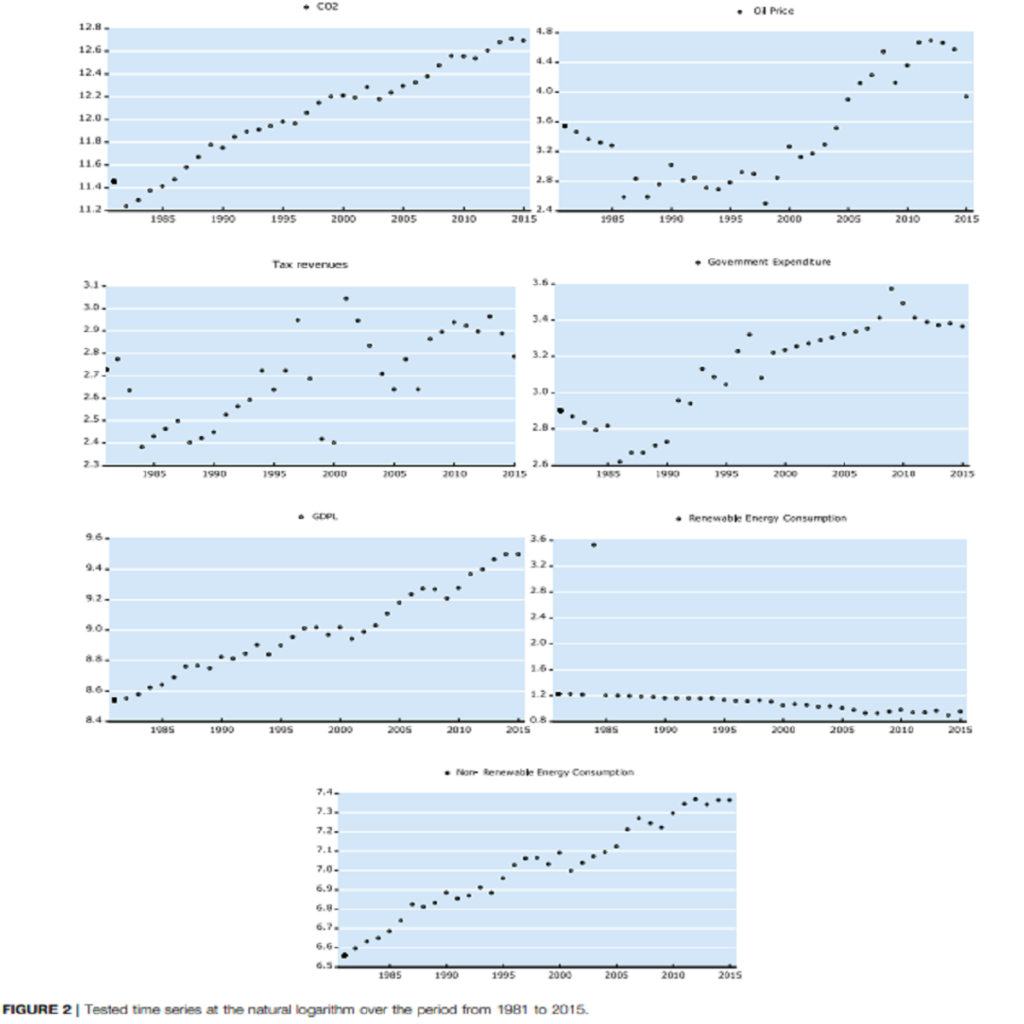
In the current empirical literature, the possible influence of oil price on environmental degradation through fiscal policy instruments has been ignored. To address this gap, this study explores the influence of oil price on the environmental degradation in Turkey through fiscal policy instruments, using a novel methodology of bootstrap ARDL approach. The FMOLS, CCR, DOLS, and ARDL models are used to examine the long-run linkage among the tested variables. The findings from estimating models demonstrated that government expenditures affected positively environmental degradation in Turkey. In contrast, the taxation revenues affected negatively environmental degradation. Furthermore, the empirical outcomes affirm that prices of oil have a powerful effect on the levels of Turkey’s environmental pollution through taxation revenues, energy, and GDP factors. The study suggests that the Turkish policymakers should design policies to avoid any undesirable impacts of the spillover effects of the oil price on the environment using fiscal policy channels. In this sense, the government in Turkey should design a framework that includes financial incentives such as low taxation rates on green energy investment. In addition, the policy markets in Turkey should start to use the carbon taxes policy, which is one of the most efficient tools to reduce the level of environmental pollution.
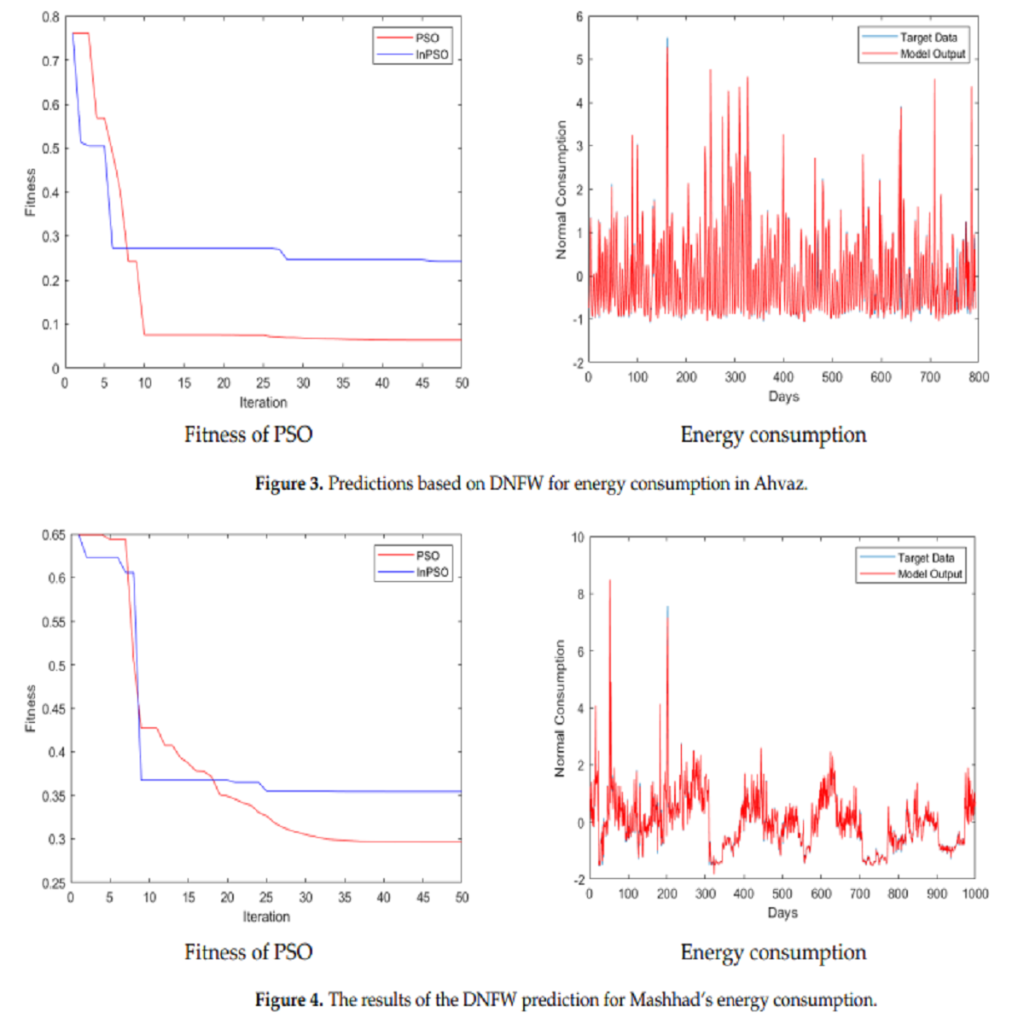
Energy has been one of the most important topics of political and social discussion in recent decades. A significant proportion of the country’s revenues is derived from energy resources, making it one of the most important and strategic macro policy and sustainable development areas. Energy demand modeling is one of the essential strategies for better managing the energy sector and developing appropriate policies to increase productivity. With the increasing global demand for energy, it is necessary to develop intelligent forecasting methods and algorithms. Different economic and non-economic indicators can be used to estimate the energy demand, including linear and non-linear statistical methods, mathematics, and simulation models. This non-linear relationship between these indicators and energy demand has led researchers to search for intelligent solutions, such as artificial neural networks for non-linear modeling and prediction. The purpose of this study was to use a deep neural network with fuzzy wavelets to predict energy demand in Iran. For the training of the presented components, a hybrid training method incorporating both an inline PSO and a gradient-based algorithm is presented. The provided technique predicts energy consumption in Tehran, Mashhad, Ahvaz, and Urmia from 2010 to 2021. This study shows that the presented method provides high-performance prediction at a lower level of complexity.
In comparison to the competitors, engineers must provide quick, low-cost, and dependable solutions. The advancement of intelligence generated by machines and its application in almost every field has created a need to reduce the human role in image processing while also making time and labor profit. Lepidopterology is the discipline of entomology dedicated to the scientific analysis of caterpillars and the three butterfly superfamilies. Students studying lepidopterology must generally capture butterflies with nets and dissect them to discover the insect’s family types and shape. This research work aims to assist science students in correctly recognizing butterflies without harming the insects during their analysis. This paper discusses transfer-learning-based neural network models to identify butterfly species. The datasets are collected from the Kaggle website, which contains 10,035 images of 75 different species of butterflies. From the available dataset, 15 unusual species were selected, including various butterfly orientations, photography angles, butterfly lengths, occlusion, and backdrop complexity. When we analyzed the dataset, we found an imbalanced class distribution among the 15 identified classes, leading to overfitting. The proposed system performs data augmentation to prevent data scarcity and reduce overfitting. The augmented dataset is also used to improve the accuracy of the data models. This research work utilizes transfer learning based on various convolutional neural network architectures such as VGG16, VGG19, MobileNet, Xception, ResNet50, and InceptionV3 to classify the butterfly species into various categories. All the …
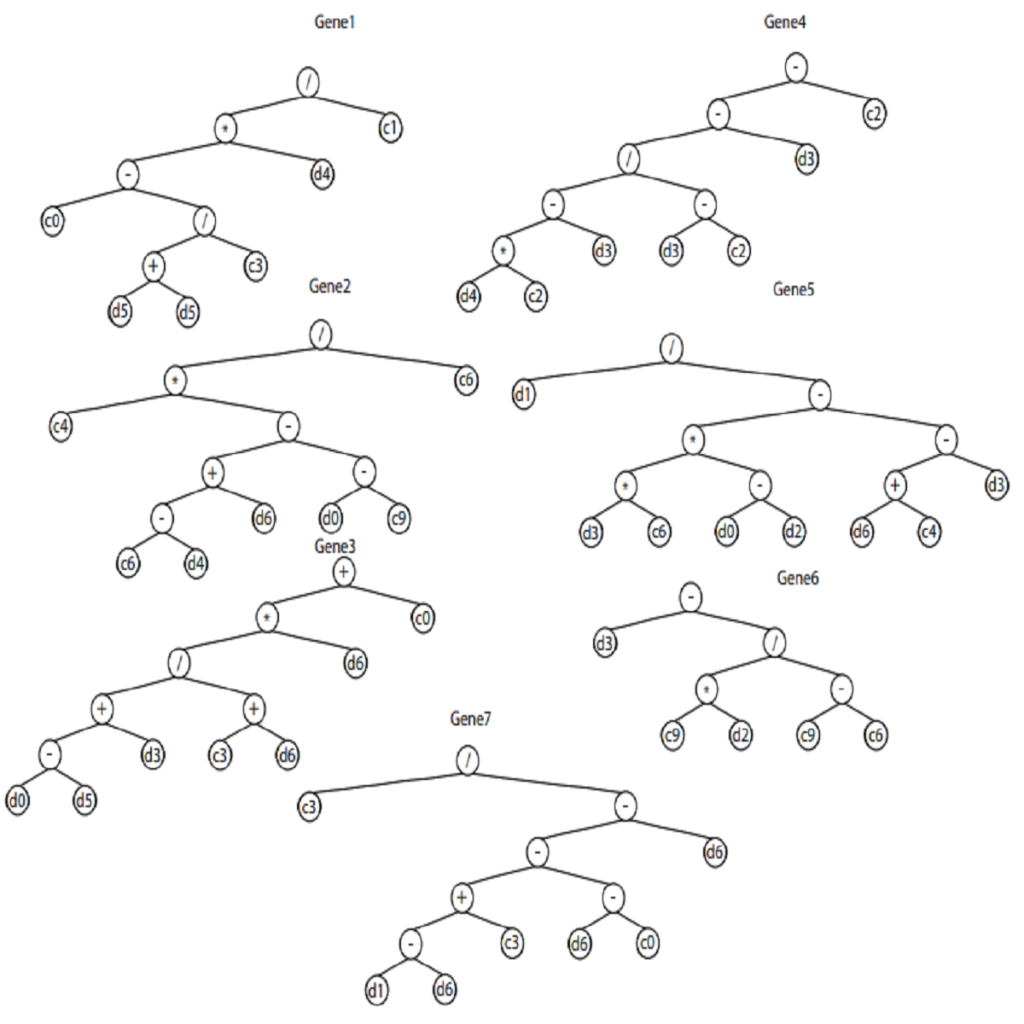
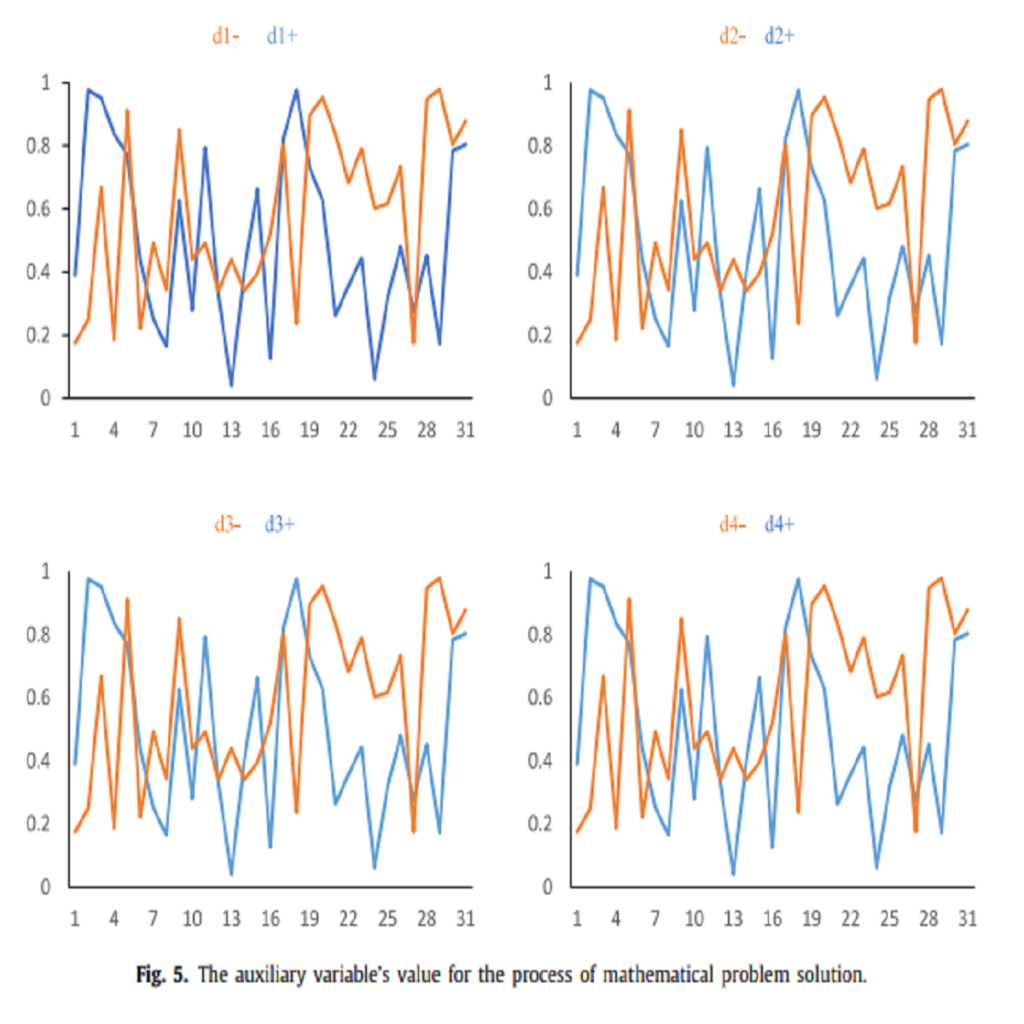
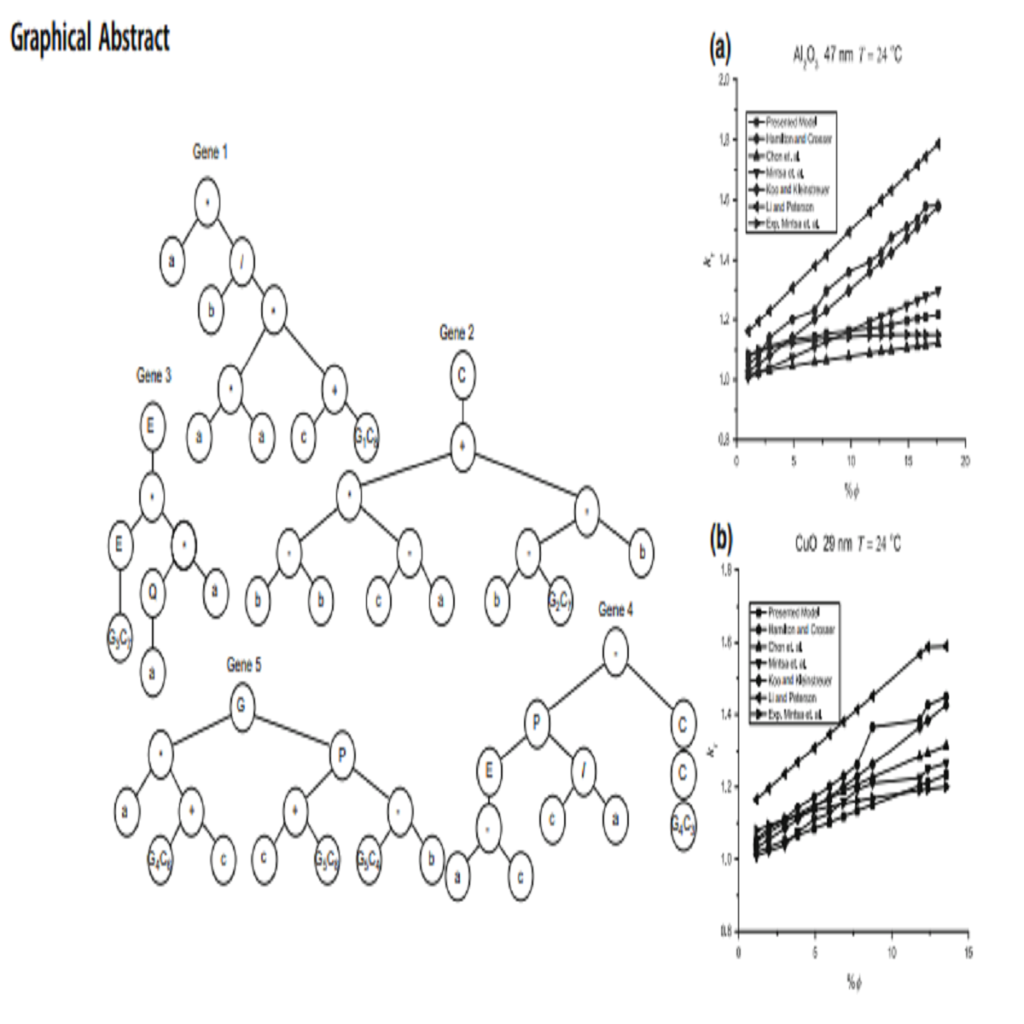
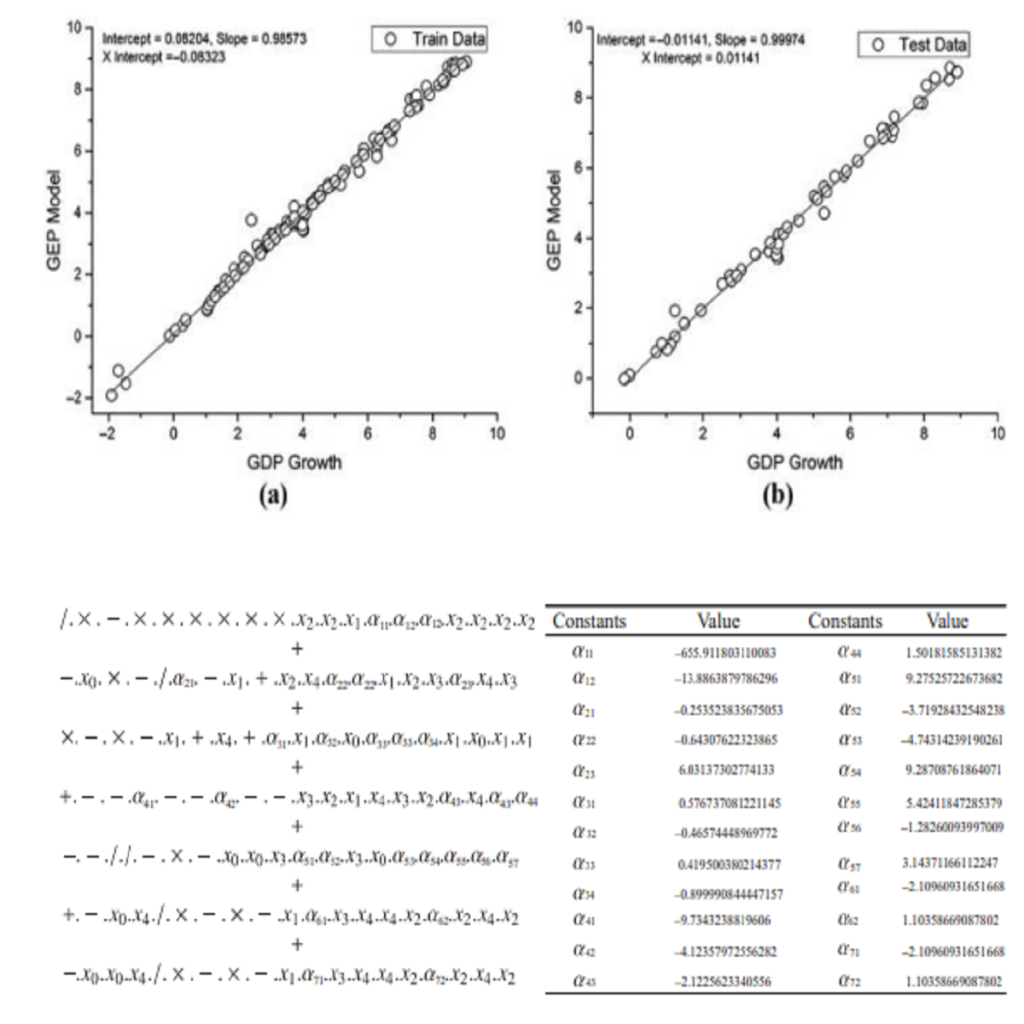
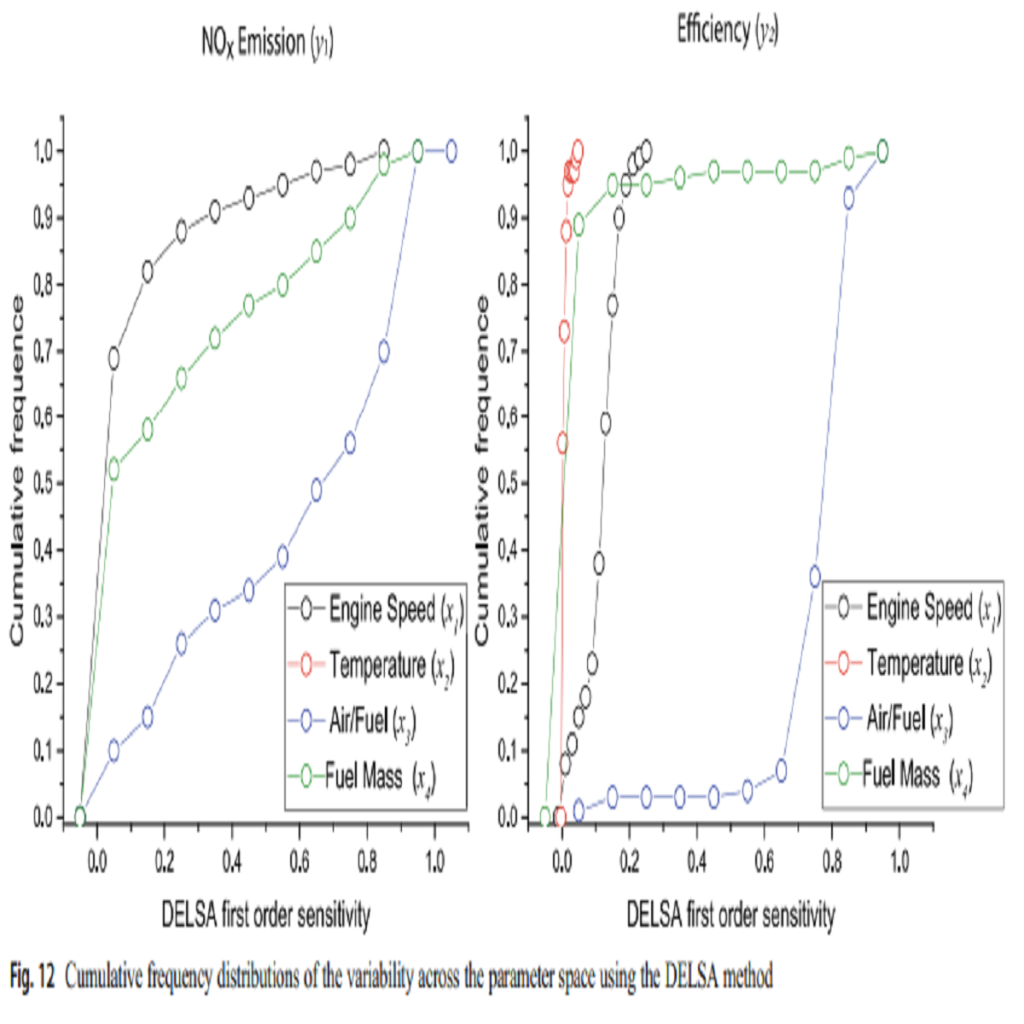
This paper involves discovering effective and better reaction of the diesel engine at various velocities by having ideal values in a short period. Therefore, gene expression programming is used for modeling and presenting governing expression for the related factors. The effective parameters consist of engine speed, intake air temperature, rate of air over fuel, fuel mass, NOx emission, mechanical efficiency, and immediate infusion diesel engine used as a part of demonstrating. Gene expression programming and its values exactly predict output results and present precise formula. Moreover, the sensitivity analysis was performed to recognize the effectiveness of the factors for reducing NOx and increasing mechanical efficiency. In the sensitivity analysis, the methods such as partial correlation coefficient, standard regression coefficient, and the Sobol’-Jansen and distributed evaluation of local sensitivity analysis are …
Chen Ke, Ng Tee Weng, Yifan Yang, Zhang Ming Yang, Putra Sumari, Laith Abualigah, Salah Kamel, Mohsen Ahmadi, Mohammed AA Al-Qaness, Agostino Forestiero, Anas Ratib Alsoud
Mango is one of the well known tropical fruits native to south asia and currently there are over 500 varieties of mangoes known. Depending on the variety, mango fruit can be varied in size, skin color, shape, sweetness, and flesh color which may be pale yellow, gold, or orange. However, sometimes it is difficult for us to differentiate what type of mango it is. Thus, in this paper, four types of mango classification approach is presented. Thus, we are going to use convolutional neural network (CNN) algorithm and transfer learning methods (VGG16 and Xception) to train on the 1000 mango images collected and obtain a deep learning model which is able to classify four types of mango (Alampur Baneshan, Alphonso, Harum Manis and Keitt) automatically. In summary, the objective in this paper is to develop a deep learning algorithm to automatically classify four types of mango cultivar.
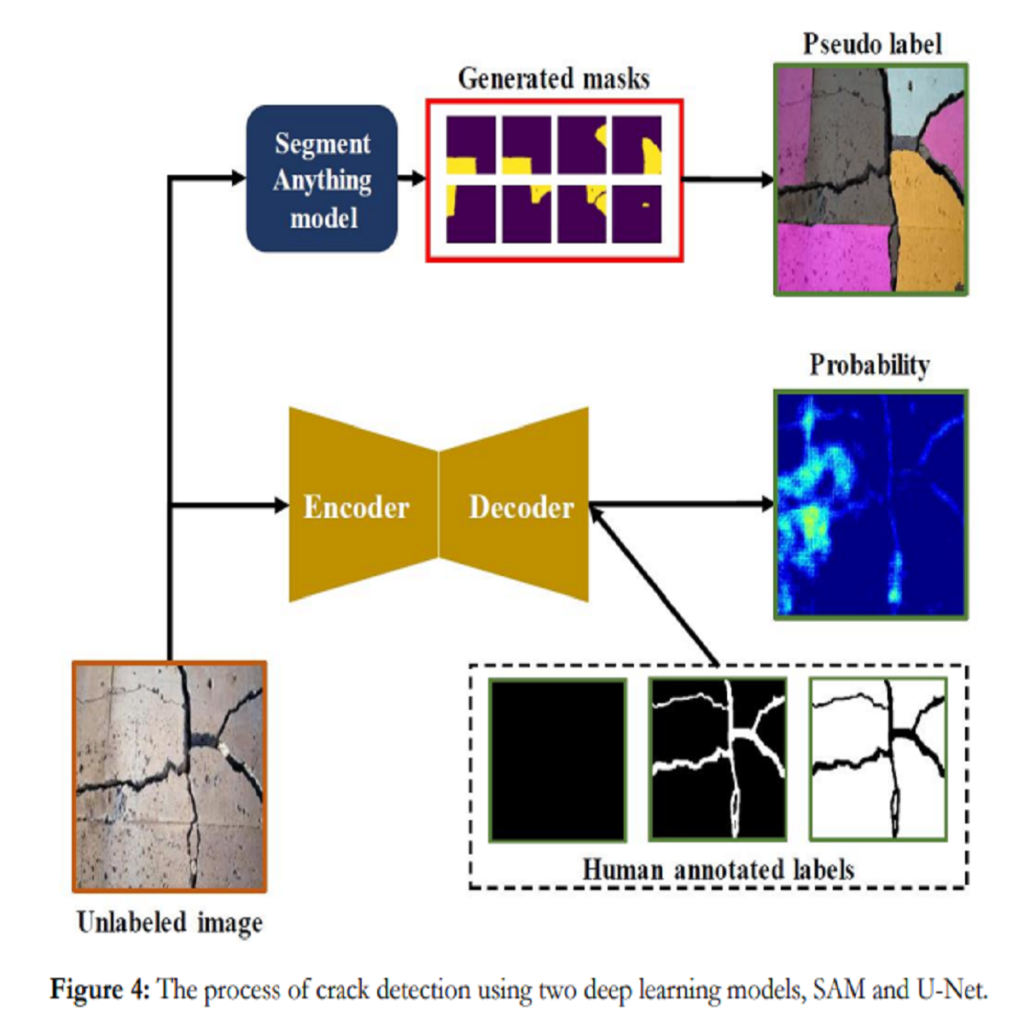
This research assesses the performance of two deep learning models, SAM and U-Net, for detecting cracks in concrete structures. The results indicate that each model has its own strengths and limitations for detecting different types of cracks. Using the SAM’s unique crack detection approach, the image is divided into various parts that identify the location of the crack, making it more effective at detecting longitudinal cracks. On the other hand, the U-Net model can identify positive label pixels to accurately detect the size and location of spalling cracks. By combining both models, more accurate and comprehensive crack detection results can be achieved. The importance of using advanced technologies for crack detection in ensuring the safety and longevity of concrete structures cannot be overstated. This research can have significant implications for civil engineering, as the SAM and U-Net model can be used for a variety of concrete structures, including bridges, buildings, and roads, improving the accuracy and efficiency of crack detection and saving time and resources in maintenance and repair. In conclusion, the SAM and U-Net model presented in this study offer promising solutions for detecting cracks in concrete structures and leveraging the strengths of both models that can lead to more accurate and comprehensive results.
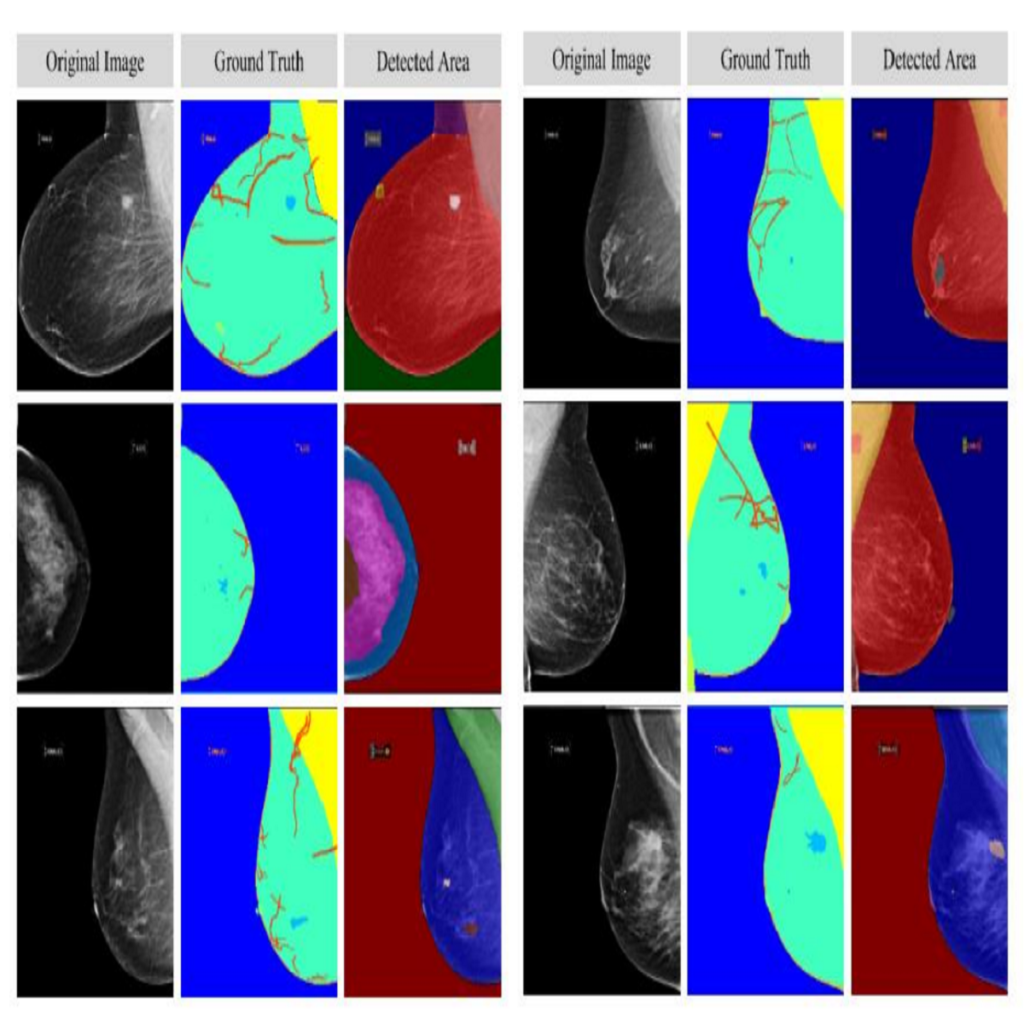
In this study, the main objective is to develop an algorithm capable of identifying and delineating tumor regions in breast ultrasound (BUS) and mammographic images. The technique employs two advanced deep learning architectures, namely U-Net and pretrained SAM, for tumor segmentation. The U-Net model is specifically designed for medical image segmentation and leverages its deep convolutional neural network framework to extract meaningful features from input images. On the other hand, the pretrained SAM architecture incorporates a mechanism to capture spatial dependencies and generate segmentation results. Evaluation is conducted on a diverse dataset containing annotated tumor regions in BUS and mammographic images, covering both benign and malignant tumors. This dataset enables a comprehensive assessment of the algorithm’s performance across different tumor types. Results demonstrate that the U-Net model outperforms the pretrained SAM architecture in accurately identifying and segmenting tumor regions in both BUS and mammographic images. The U-Net exhibits superior performance in challenging cases involving irregular shapes, indistinct boundaries, and high tumor heterogeneity. In contrast, the pretrained SAM architecture exhibits limitations in accurately identifying tumor areas, particularly for malignant tumors and objects with weak boundaries or complex shapes. These findings highlight the importance of selecting appropriate deep learning architectures tailored for medical image segmentation. The U-Net model showcases its potential as a robust and accurate tool for tumor detection, while the …
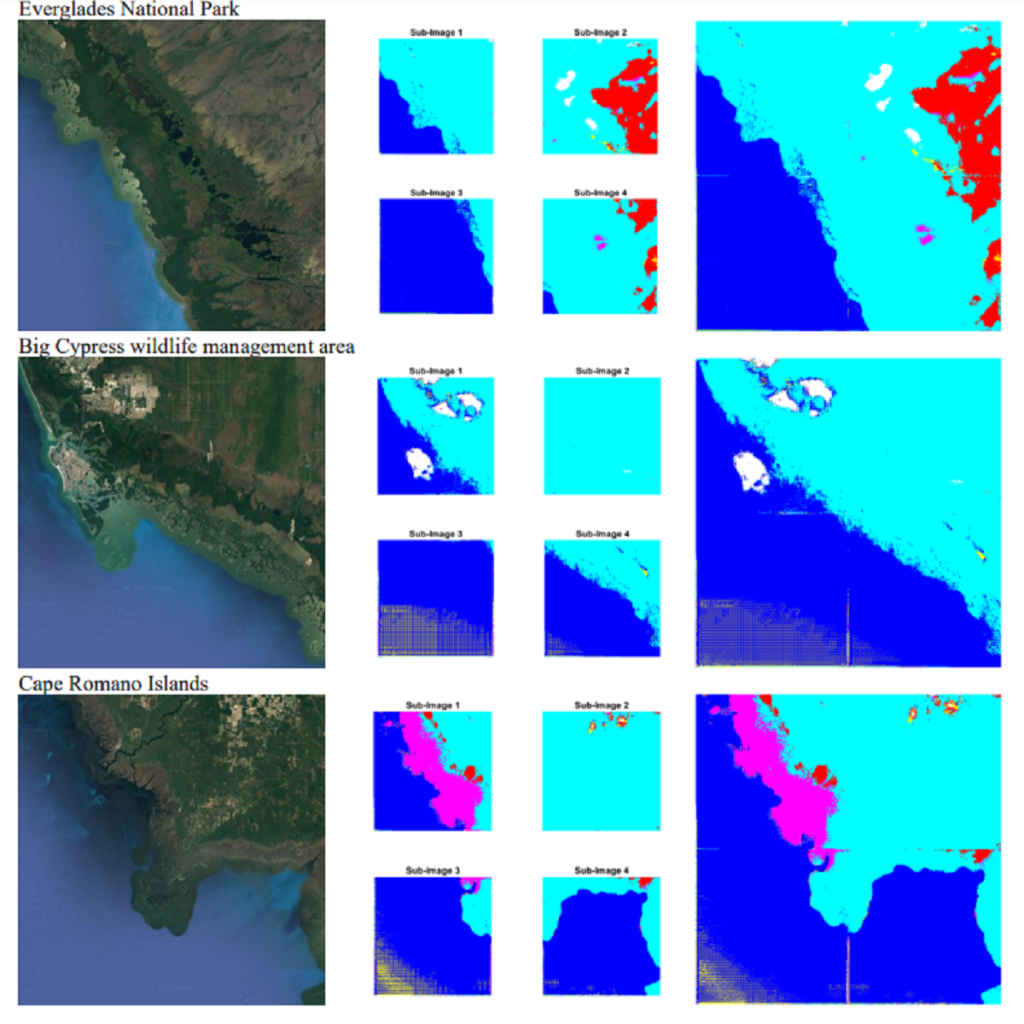
This study explores the use of a digital twin model and deep learning method to build a global terrain and altitude map based on USGS information. The goal is to artistically represent various landforms while incorporating precise elevation modifications in the terrain map and encoding land height in the altitude map. A random selection of 5000 segments from the worldwide map guarantees the inclusion of significant characteristics in the subsets, with rescaling according to latitude accounting for distortions caused by map projection. The process of generating segmentation maps involves using unsupervised clustering and classification methods, segmenting the terrain into seven groups: Water, Grassland, Forest, Hills, Desert, Mountain, and Tundra. Each group is assigned a unique color, and median filtering is used to improve map characteristics. Random parameters are added to provide diversity and avoid duplication in overlapping image sets. The U-Net network is deployed for the segmentation task, with training conducted on the seven terrain classes. Cross-validation is carried out every 10 epochs to gauge the model’s performance. The segmentation maps produced accurately categorize the terrain, as evidenced by the ROC curve and AUC values. The main goal of this research is to create a digital twin model of Florida’s coastal area. This is achieved through the application of deep learning methods and satellite imagery from Google Earth, resulting in a detailed depiction of the coast of Florida. The digital twin acts as both a physical and a simulation model of the area, emphasizing its capability to capture and replicate real-world …
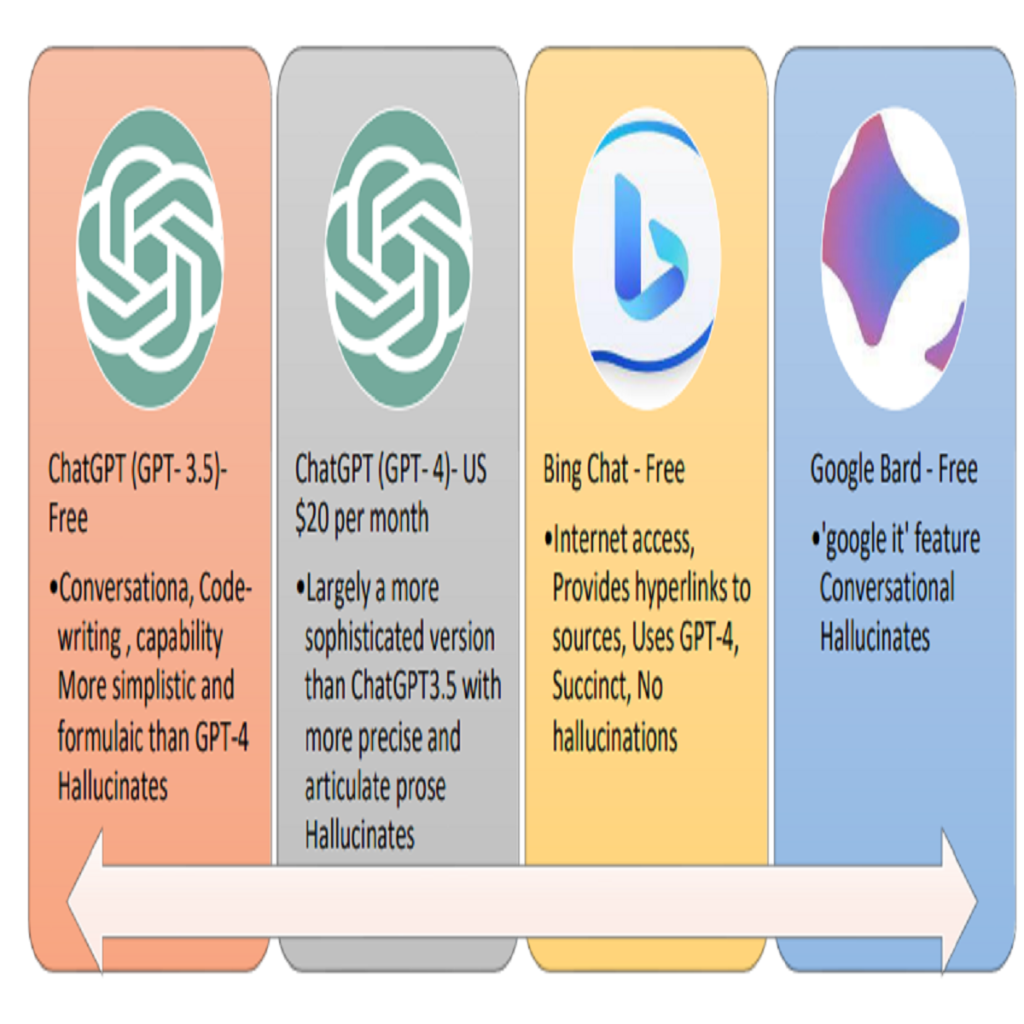
In the digital era, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in education has ushered in transformative changes, redefining teaching methodologies, curriculum planning, and student engagement. This review paper delves deep into the rapidly evolving landscape of digital education by contrasting the capabilities and impact of OpenAI’s pioneering text generation tools like Bing Chat, Bard, Ernie with a keen focus on the novel ChatGPT. Grounded in a typology that views education through the lenses of system, process, and result, the paper navigates the multifaceted applications of AI. From decentralizing global education and personalizing curriculums to digitally documenting competence-based outcomes, AI stands at the forefront of educational modernization. Highlighting ChatGPT’s meteoric rise to one million users in just five days, the study underscores its role in democratizing education, fostering autodidacticism, and magnifying student engagement. However, with such transformative power comes the potential for misuse, as text-generation tools can inadvertently challenge academic integrity. By juxtaposing the promise and pitfalls of AI in education, this paper advocates for a harmonized synergy between AI tools and the educational community, emphasizing the urgent need for ethical guidelines, pedagogical adaptations, and strategic collaborations.